Absolute Value:
Shows the distance from a point on a Number Line to 0. Absolute value is always positive. For example,Addition Terminology:

Associative Property
The property that shows that a X (b X c) = (a X b) X cCommutative Property
The property that shows that a + b = b + a, and also that a X b = b X aComposite Number
A number that is the product of two or more smaller whole numbersCounting numbers
The Counting Numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...).Distributive Property:
The property that shows that a x (b + c) = a x b + a x cDivision Terminology:

Exponential Terminology:
Factor
A counting/natural number, which when multiplied by another counting/natural number, results in a product. For instance, the factors of 6 are 1 and 6 (1 x 6) and also 2 and 3 (2 x 3).Imaginary numbers
Real numbers multiplied by the square root of -1, which is symbolized with the letter i.Integer numbers
The positive and negative whole numbers (...,-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...)Irrational numbers
Numbers along a number line that can't be expressed as the fraction of two integers (ex. pi).Multiple
A counting/natural number that is the product of a given factor. For instance, some multiples of 2 are 2 (2 x 1), 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 8 (2 x 4), and 10 (2 x 5)Multiplication terminology

Natural numbers
The Natural Numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...). Sometimes this set of numbers starts at 0 (and so 0, 1, 2, 3,...). It's something that no one agrees on and so it's best to know, when this term is used, if 0 is to be included.
For the purposes of this blog, I will use Natural Numbers to mean the Counting Numbers (I'll use Natural Numbers because of its symbol N).Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
This is the order in which we work expressions/equations:
- P = Parentheses (also known as Brackets)
- E = Exponentials
- M = Multiplication (same weight as Division)
- D = Division (same weight as Multiplication)
- A = Addition (same weight as Subtraction)
- S = Subtraction (same weight as Addition)
A whole number greater than 1 that is not the product of two or more smaller whole numbers.
Rational numbers

Variable
Numbers that can be expressed as the fraction of two integers, with the divisor being non-zero.Real numbers
All the numbers along a number line and is comprised of both Rational and Irrational numbers.Subtraction terminology:

Variable
A letter or symbol used to indicate a placeholder for either a single number or range of numbers.Whole numbers
The counting numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...). The Whole Numbers include 0 and the natural numbers sometimes do include 0 and sometimes don't.
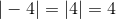

No comments:
Post a Comment
Hi there - I'm glad to see you are thinking about or maybe even getting ready to post a comment! I moderate all comments so please be patient while I hit the "ok" button on yours. Feel free to make suggestions on web resources to add, directions the entries should go,... whatever. And thanks again for leaving some feedback!